LIGHTING TERMS
LIGHTING TERMS
Directional light that is used to emphasize or highlight a particular object.
Ampere:
The standard unit of measurement for electric current that is equal to one coulomb per second. It defines the quantity of electrons moving past a given point in a circuit during a specific period.
Abbreviation – Amp Coulomb:
A unit of electrical charge, defined as the amount of electric charge transported by a current of 1 ampere in 1 second.
Ballast:
A device used to supply sufficient voltage to start and operate Fluorescent and HID lamps while limiting and regulating the lamp’s current during operation.
Bayonet Cap Base:
A type of lamp base with a pin on either side, which locks the lamp into place when placed in the lamp socket.
Beam Angle:
The degree of width that light emanates from a light source.
Bollard:
An outdoor light fitting that is a very sturdy vertical post with the light source located at or near the top. Bollards are typically used to light up walkways in commercial areas.
Brick Lights:
A light fitting that can be recessed in a brick wall to light up a walkway, step, landing, or pathway.
Bulb:
Another term for a lamp.
Cathode:
An electrode that emits electrons. A fluorescent lamp cathode emits or discharges electrons to the cathode at the other end of the lamp.
Electrons:
A negatively charged component of an atom.
Colour Rendering Index (CRI):
A measure of the ability of a light source to reproduce the colour of various objects faithfully in comparison with an ideal or natural light source. The CRI simply rates colour rendering out of 100; the higher the index, the better the colour rendering.
Colour Temperature:
A measure of how warm or cool the light given off by a lamp appears. ‘Warm’ colours appear tinged with yellow and generally feel soft and cosy. Cool colours are tinged with blue and appear whiter, making them a more ‘honest’ and unforgiving light, more suitable for working environments than relaxing. Light is measured through the Kelvin Temperature scale.
Compact Fluorescent Lamp (CFL):
Often used as an alternative to incandescent lighting. They have high colour rendering and a lamp life about five times longer than incandescent lamps.
Cove Lighting:
A form of indirect lighting built into ledges, recesses, or valences in a ceiling or high on the walls of a room.
Diffuser:
A translucent piece of glass or plastic sheet that shields the light source in a fixture. The light transmitted through the diffuser is redirected and scattered.
Dimmer:
A device in an electrical circuit used for varying the brightness of a lamp in a lighting installation.
Direct Current (DC):
An electric current that has no alterations.
Downlights:
A light fixture usually completely recessed into the ceiling that concentrates most of the light in a downward direction. It may feature an open reflector and/or a shielding device.
Edison Screw Base:
A lamp base that screws into its matching socket when rotated clockwise.
Efficacy:
A metric used to compare light output to energy consumption. Efficacy is measured in lumens per watt.
Electronic Ballast:
A ballast that uses semiconductor components to increase the frequency of fluorescent lamp operation.
Emergency Lighting:
Lighting used when the normal lights fail, such as exit lights.
Flicker:
Variation in light intensity due to 50 Hz operation. It can cause eye strain and fatigue due to stroboscopic effects.
Floodlight:
A broad-beamed, high-intensity artificial light source generally used for industrial and commercial applications.
Fluorescent Lamp:
A light source consisting of a tube filled with argon, along with krypton or other inert gas. A phosphor coating on the inside of the glass tubing transforms some of the ultraviolet energy created inside the lamp into visible light when electrical current is applied.
Footcandle:
The English unit of measurement of the illuminance (or light level) on a surface. One footcandle is equal to one lumen per square foot.
Frequency:
The number of times per second that an alternating current system reverses from positive to negative and back to positive, expressed in cycles per second or hertz (Hz).
Glare:
Direct glare is caused by light coming directly to the eye from a light source. Indirect glare is light reflected from a surface in the direction of the eye. Both can harm vision and cause visual discomfort, annoyance, or loss of visual performance.
GU10 Lamp:
These lamps have a turn-and-lock base, so they cannot be accidentally interchanged with low-voltage lamps. Their filaments are finer, making them more fragile than those used in low-voltage lamps and producing far less lumen output. LED lamps have been developed as GU10 to be operated directly on mains voltage, performing similarly to low-voltage lamps. They can house electronic drivers directly off the mains power and perform more efficiently, with dimmable options using standard residential phase-cut dimmers.
Halogen Lamp:
A type of incandescent lamp that contains halogen gases, which slow down the evaporation of the tungsten filament.
High-Bay:
Lighting used in industrial applications where the ceiling height is greater than 20 feet.
High Intensity Discharge Lamp (HID):
A generic group of lamps consisting of mercury, metal halide, and high-pressure sodium lamps.
Illuminance:
The amount of light arriving at a surface, expressed in lumens per unit area; 1 lumen per square foot equals 1 footcandle, while 1 lumen per square metre equals 1 lux.
Ingress Protection Ratings (IP Ratings):
Used to specify protection from the environment.
First IP Number – Protection against Solid Objects:
| IP Number | Solid Object Protection | IP Number | Water Protection |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | No special protection | 0 | No protection |
| 1 | Protected against solid objects up to 50mm (e.g., hands) | 1 | Protected against vertically falling drops of water |
| 2 | Protected against objects up to 12mm (e.g., fingers) | 2 | Protected against direct sprays of water up to 15° from vertical |
| 3 | Protected against solid objects over 2.5mm (tools, wires) | 3 | Protected against direct sprays of water up to 60° from vertical |
| 4 | Protected against solid objects over 1mm (tools, small wires) | 4 | Protected against water sprayed from all directions – limited ingress permitted |
| 5 | Protected against dust, limited ingress (no harmful deposits) | 5 | Protected against low-pressure jets of water from all directions – limited ingress permitted |
| 6 | Totally protected against dust | 6 | Protected against temporary flooding of water (e.g., ship decks) – limited ingress permitted |
| 7 | Protected against immersion between 15cm and 100cm | ||
| 8 | Protected against long periods of immersion under pressure |
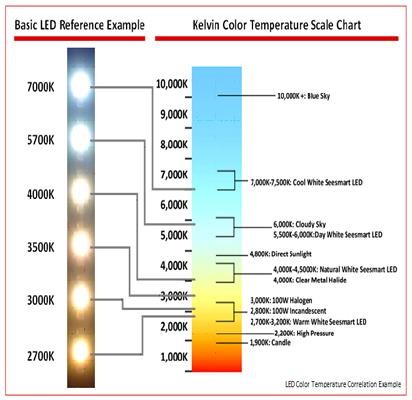
Kelvin Temperature Scale
The way we measure light is through the Kelvin Temperature scale. This standardized colour scale is created by heating a theoretical black body, starting out at zero degrees Kelvin (Absolute zero). As the body heats up, it glows, like any other object would. As the heat increases, the colour changes, appearing first dark red, then yellow, moving through the visible colours of the spectrum until it reaches blue and violet.
Light Emitting Diode
Light Emitting Diode, also known as LED, is a small electronic device that lights up when electricity is passed through it. LEDs have a very long life and come in a variety of colours, the most common being Warm White, Cool White, Red, Green, and Blue.
Low Voltage Lamp
Low voltage lighting systems usually operate on 12 volts and 24 volts. These systems use a transformer (electronic or magnetic) to convert the incoming voltage (usually 240 volts) to 12 or 24 volts.
Lumen
A unit of light flow. The lumen rating of a lamp is a measure of the total light output of the lamp.
Here is a table representing the light output (lumens) and corresponding wattage for LEDs, CFLs, and Incandescent bulbs:
| Light Output (Lumens) | LEDs (Wattage) | CFLs (Wattage) | Incandescents (Wattage) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 450 | 4 – 5 W | 8 – 12 W | 40 W |
| 300 – 900 | 6 – 8 W | 13 – 18 W | 60 W |
| 1100 – 1300 | 9 – 13 W | 18 – 22 W | 75 – 100 W |
| 1600 – 1800 | 16 – 20 W | 23 – 30 W | 100 W |
| 2600 – 2800 | 25 – 28 W | 30 – 55 W | 150 W |
The metric unit of measurement for illuminance of a surface. One lux is equal to one lumen per square meter.
Mercury Vapour Lamp:
A type of high-intensity discharge (HID) lamp that uses mercury in an excited state to produce light, most of which is produced by radiation from mercury vapour.
Metal Halide Lamp:
A HID lamp that produces light by radiation from certain metallic vapours when supplied with electricity from a ballast.
MR16 Lamp:
MR16 lamps contain single-ended quartz halogen filament capsules with a multifaceted reflector (MR); a pressed glass reflector with the inside surface composed of facets and covered by a reflective coating. These facets provide optical control by gathering the light from the filament to create a concentrated beam of light. The reflective coating can be either Dichroic or Aluminium. Most MR16 lamps are operated using voltages lower than 120 volts, typically 12V. MR16 lamps can be dimmed through commercially available dimmers for low voltage loads.
Pendant Lighting:
Pendant lights can provide both task and general lighting, equipped with shades or globes to avoid glare. They are suspended from the ceiling over dinette tables, kitchen counters, or other work areas.
Power:
The rate at which energy is taken from an electrical system or dissipated by a load, expressed in watts (W); power that is generated by a utility is typically expressed in volt-amperes (V-A).
Reflector:
A device used to redirect the light by the process of reflection.
Starter:
A device used with a ballast to start and preheat fluorescent lamps.
Transformer:
An electrical device that transforms the line voltage of a facility into the voltage that a low-voltage lighting system requires.
Vandal Resistant:
Fixtures with rugged housing, break-resistant type shielding, and tamper-proof screws.
Volt:
A volt is the potential difference that will cause 1 ampere to flow through one ohm of resistance.
Voltage:
The standard metric unit of measurement for electrical potential. It defines the force or pressure of electricity.
Watt:
Watt is the unit for measuring electrical power. It defines the rate of energy consumption by an electrical device when it’s in operation. It is defined by the current voltage. The energy cost of operating an electrical device is calculated as its wattage times the hours of use.
